|
Performance consulting focuses on helping organizations increase productivity by strategically linking
individual performance improvement to enhanced organizational results.
As performance consultants we provide expertise to help organizations
identify individual performance requirements necessary for attaining organizational goals and work to uncover and overcome the underlying reasons for any performance deficiencies. We work collaboratively
with management to employ methodologies to identify gaps between current
and desired performance and recommend appropriate initiatives for bridging those gaps.
Our approach focuses on improving the personal performance of individuals at all levels of an
organization from the lowest level worker to that of the CEO. In doing so, we address a wide range of elements
and factors within an organization that can have a direct impact on individual performance. These elements
and factors fall into the three general domains of people, processes and strategy.
Performance consulting is not simply about improving workers’ knowledge and skills. Rather,
it looks at the entire range of organization functions that impact individual worker performance.
Knowledge and skills
are frequently the first area of focus for performance improvement initiatives, but regrettably, frequently the wrong place
to start. When people are perceived by supervisors to be performing below expected levels, the deficiency
is often characterized as a “training issue”
and the organization’s training function is called in to implement a learning initiative to “fix the problem.”
Training can often play an important role in a performance improvement solution, and there certainly will be times
when it is the preferred solution. Frequently, however, training is an inappropriate solution, and an effective
situation analysis would show that the root cause of the identified performance deficiency is not one that can be effectively
corrected by training. Even if the underlying cause is a knowledge/skills issue, it may be some other aspect of
the knowledge management continuum other
than training that deserves attention. more about Knowledge Management
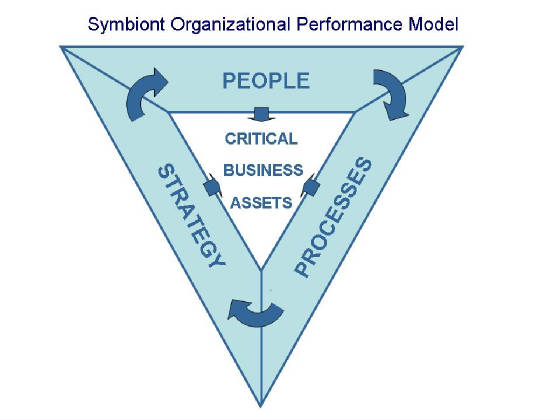
Model for Organizational Performance
The
overall level of an organization’s performance can be described in basic terms as the cumulative
impact of three general operational components—people, processes and strategy—on the organization’s critical
business assets.
 Critical Business Assets
An
organization’s critical business assets comprise the primary means or resources employed to develop and deliver the
products and services that customers buy. Examples of critical business assets can include tangible elements such as raw materials,
equipment, buildings and natural resources as well as intangible assets, often referred to as intellectual capital, such as proprietary technology, patents, trademarks, copyrights,
and other specialized knowledge. Critical business assets usually define the very nature of a business. They
are to be leveraged through expert professional management by individuals who are specialists in the specific critical assets
of a particular enterprise. An organization’s strategy, processes and people capabilities must be
effectively designed and developed to take maximum advantage of an organization’s critical business assets.
Additionally each of these three elements needs to be aligned in a manner that is mutually supportive and complementary.
Performance consultants can provide critical insights to help organizations accomplish this objective.
People The contributions of the
people who run an organization are central to the organization’s overall performance levels. The abilities demonstrated by an organization’s workers are reflected by the sum total of their inherent
talents plus the knowledge, skills and attitudes that workers bring to a position or develop on the job. The abilities of workers can be categorized as an organization’s human capital and is the source of an organization’s
creativity and innovation. Human capital is usually considered to be an intangible asset to organizations
because is difficult to evaluate and quantify so it never appears as a line on a financial statement. As
a result, it is often undervalued and ineffectively managed, much to the detriment of overall organizational performance.
Unlike tangible assets such as buildings, equipment and money, human capital is always
owned by the individuals who possess it, and can “walk out the door” unless it is recorded in some tangible form, or is incorporated into organization's procedures and structure through knowledge management systems. Well-designed initiatives for maximizing the contribution of
an organization’s people can significantly increase and preserve their contribution to business results. Performance
consultants improve organizational results by focusing on ways to improve the performance outputs of individual workers and
the specific organizational processes that directly and indirectly affect them.
Processes An organizational process consists of a series of tasks, operations or functions through which and within which work activities are carried out in organizations.
Processes focus specifically on how work is done within organizations and encompass both formal and informal
policies, procedures, and practices that pertain to particular organizational functions. Processes can be organized into
five general categories:
- Operational
Processes - processes that describe an organized series of progressive steps, tasks and actions required for
the execution of core organizational functions and
jobs (e.g., a manufacturing process).
- Business
Processes - processes that describe the policies and procedures for how an organization interacts with customers (e.g.,
sales, order processing).
- Leadership Processes - processes that govern the implementation
of activities relating to an organizations leadership and the management of its people (e.g., strategic planning,
reporting structures and human resource policies and procedures.
- Support Processes – processes that provide
organizational support services for the overall effective operation of an organization (e.g., accounting, training, information
technology services).
- Cultural Processes – informal processes consisting of collections of values, beliefs and behavioral
standards shared by people within an organization that control the way they interact with one another and with outside
stakeholders.
Processes, whether integral to a particular job or ancillary to it, that are not properly organized and managed to
support optimum worker performance can be significant contributing factors to sub-standard organizational results. Mandated
reports for example, may be unnecessarily cumbersome or even totally unnecessary) and time-consuming, and time devoted to
completing them may detract from valuable work time that could be more productively used otherwise. The same can be said for
meetings that may be of very limited value to many of the attendees. It is often difficult for managers to accurately assess the
reasons for a lack of desired organizational results because they may be intimately involved in one or more of the elements
impeding worker performance and are unable to see the forest because of the trees so to speak, and/or may have vested
interests in keeping things as they are. Performance consultants bring objectivity and an outside perspective to the workplace.
Strategy Strategy can be defined as the
effective application of a limited set of resources in a clearly defined manner through specific activities to achieve organizational
goals. Strategy defines what an organization aims to achieve (vision) and the manner and approach it will employ to achieve it (mission). It
may also include elements relating to organization values and behavioral norms. Strategic
behavior generally involves doing different things than competitors or doing similar things in a different way to gain an
advantage. It is usually viewed within the context of outperforming the competition but can also be applied to overcoming
obstacles of a non-competitive nature that stand in the way of success (e.g., avoiding a potentially costly union strike).
An effective
strategy is critical to effective organizational performance because it articulates an organization’s plan for overcoming
the challenges presented by external factors such as competitive activity, market characteristics,
economic conditions and government regulations. Additionally, effective strategy embodies the aims and focuses of
organizational processes and characterizes the attitudes and values of its people. Helping organizations
plan, develop and execute effective strategy is a major focus of performance consulting.
Model for Performance Improvement The organizational performance model described above focuses on the impact
of the contributions of people, strategy and processes on an organization’s critical business assets
as well as the impact of these factors on each other. Strategy and processes clearly are important
elements of an organizational performance equation. However, it is an organization’s workers (people)
who ultimately deliver the organization’s results. While, strategy and processes in and of themselves
clearly have major impacts on the success with which critical business assets are managed, they can also indirectly influence
the performance levels of an organization’s people. Therefore, elements of strategy and process must be factored into
any performance improvement strategies for individual workers. The following performance improvement model
effectively captures this concept.
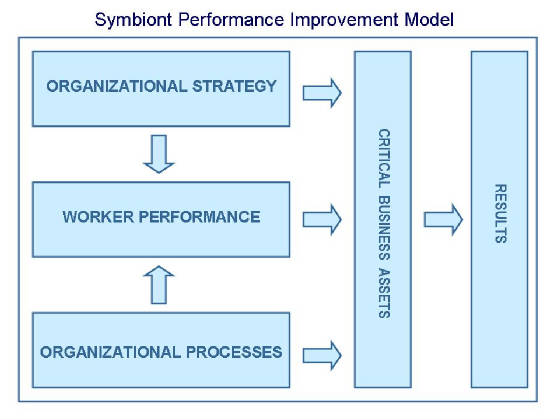 The role of a performance consultant is to
help organizations enhance their overall business results by improving the productivity of its people. Through
the use of the performance improvement model described above, performance consultants can categorize the elements that drive
performance into those that are contained within the individual worker—personal performance inputs and those that emanate from the work environment—organizational performance inputs which
can have either a direct or indirect impact on worker productivity.
Personal Performance Inputs Personal performance inputs comprise factors such as knowledge and skills,
attitudes, personal goals and motivation. These factors individually and in
combination, are the principle determinants of the quality of individual worker performance. While it is
almost universally recognized that a worker’s employer has at least as much responsibility for the development
of worker knowledge and skills as the does the worker, inputs such as an employee’s, attitude, motivation and personal
goals are usually considered to be the sole responsibility the worker. The realization that organizations can and should also
focus on these elements can bring about a dramatic positive change in overall organizational results.
Organizational Performance Inputs
The inputs affecting worker performance that derive from the work environment (the organization itself) rather
than from within the worker can generally be categorized as being elements of either strategy or processes. As depicted in
the Symbiont Performance Improvement Model, strategy and processes can influence the level of individual worker productivity
as well as having a direct impact on organizational results. Example of organizational inputs would be
worker selection and training (processes) and the level of worker empowerment (strategy). learn about the “success formula”
D.I.AL.O.G. Organizational Assessment Instrument
Successful organizations are continually looking
for ways and areas to improve in order to gain a competitive advantage. We know that the interrelationships between the
various processes within an organization are important determinants of overall success. When an organization's processes
are aligned with organizational strategy, the needs and aspirations of its people and with each other, the greater is the
probability of success.
D.I.AL.O.G. (Data Indicating Alignment
of Organizational Goals) is an organizational assessment tool that provides information as to how well critical elements of
process are working together to business strategic goals. It also helps identify elements that are working against an
organization's objectives. Our approach is unique in that we measure the interrelationships of critical elements
which serve as predictors of future strength. D.I.AL.O.G. focuses on relevant activities to identify ways to generate
improved organizational productivity. more about D.I.AL.O.G
The Symbiont Performance Consulting
Process
The following represents our basic approach to a performance consulting project: Assessment Phase 1.
Identify organizational performance objectives 2.
Identify required worker performance competencies 3. Identify required
worker & organizational best practices
4.
Identify worker performance and best practices gaps 5.
Perform gap-analysis on current personal inputs to worker performance 6. Perform gap-analysis on current organizational inputs to worker performance 7. Determine the causes of personal input and
organizational input gaps 8.
Generate learning sponsor buy-in to assessment findings
Intervention Development Phase
1.
Develop personal (worker/people-focused) performance
improvement initiatives 2. Develop organizational (process/strategy-focused ) performance improvement initiatives 3. Generate management support for intervention plan Intervention Implementation Phase 1. Set
intervention priorities 2. Generate target group intervention buy-in 3. Deliver
performance improvement interventions 4.
Measure and assess intervention impacts
Please contact us for details about our performance consulting capabilities and to request a no obligation
performance needs assessment.worksheet 860-283-9963 | info@symbiontnet.com
____________________________________________________________________________________________
|


